As the first quarter closed, sixteen states: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Maryland, Mississippi, New Mexico, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, and Wyoming have adjourned sine die. By the end of April, close to half of all states will not be in session.
Of those that have concluded, the Virginia General Assembly had the highest number of bills enacted into law, with 809 signed by the state’s newly elected governor, Ralph Northam (D). Arkansas had a whopping 275 bills signed out of 281 that were introduced, which makes them the most productive based on percentage of bills introduced that ended up passing. Georgia Governor Nathan Deal (R) has only signed 23 bills but close to 300 await his action, as the deadline for him to sign bills under Georgia state law falls in mid-May.
Some takeaways from the sixteen states (Exhibit 1):
- Arkansas passed 98% of their bills
- Florida, Georgia, Maryland, and Mississippi all passed less than 10% of bills introduced
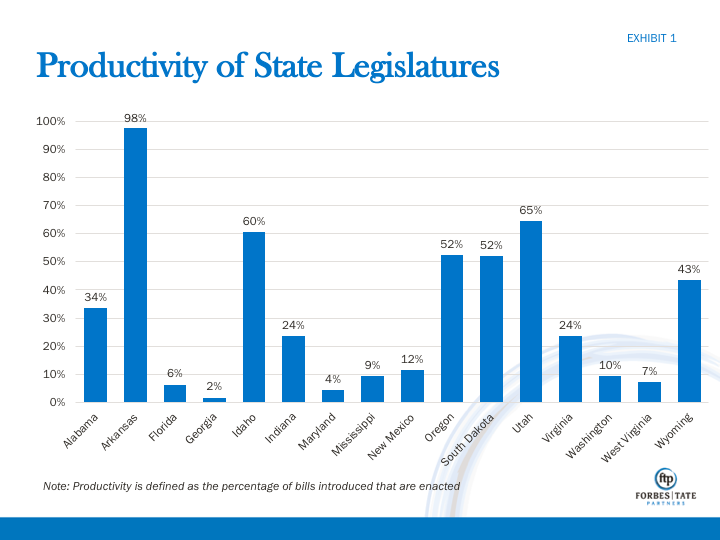
Of the 25,352 bills introduced in the sixteen states, some of the more prominent legislative trends this session have been: contentious budget battles, increases in education funding, gun initiatives, combatting the opioid crisis, and Medicaid expansion.
Contentious Budget Battles
With many states having to pass operating budgets this year, funding priorities often lead to disagreements among state lawmakers. For example, tension in Wyoming between the House and the Senate over funding construction versus schools led to a compromise to cut school funding by $27 million over the next two years. Florida’s budget process became contentious over the $400 million allocation for new mental health initiatives in schools as some superintendents felt “handcuffed.” Similar to Florida, Maryland also passed a budget with $30 million set aside for school safety, which Delegate Deborah Rey (R) argued was not enough. Lastly, Virginia’s lawmakers could not agree to a budget and have returned to Richmond for a special session.
Increases in Education Funding
With high-profile teacher strikes taking place in West Virginia and Oklahoma, other states took note and gave pay raises to teachers and increased education funding whether in biennial budget bills or standalone education bills. For example, Alabama gave a 2.5% pay increase to teachers as part of their largest education budget in a decade. Additionally, New Mexico Governor Susana Martinez (R) signed a biennial budget giving teachers a $2,000 pay increase as well as a 2.5% raise. Legislators in Mississippi also approved an $11 million increase in K-12 education funding. Finally, Washington passed a bill fully funding teachers’ salaries before the start of the 2018-2019 school year in response to last year’s State Supreme Court order on school funding.
Gun Initiatives
In the aftermath of the Parkland shooting, the issue of guns has surfaced to the top, and states are moving in different directions. Florida passed SB 7026, which raises the age of buying guns to 21. Alabama HB 435, a bill to arm teachers, passed through committee but did not come up for debate on the House floor. The measure’s sponsor, Representative Will Ainsworth (R), has called for a special session on school safety. South Dakota Governor Dennis Daugaard (R) signed a bill allowing instant background checks for one to obtain a concealed carry permit and while Vermont is still in session, Governor Phil Scott (R) has, to the objection of many gun owners in the state, signed S. 55, a bill that raises the age of purchasing to 21 and bans large capacity magazines and bump stocks. The debate on gun reforms looks poised to continue throughout the 2018 campaign season.
Combatting the Opioid Crisis
As the opioid crisis continues to harm many states, states continue to adopt laws that seek to fight it. For example, Florida HB 21, which was quickly signed by Governor Rick Scott (R), requires the co-prescription of an opioid overdose antagonist such as naloxone with certain opioid treatments. West Virginia SB 272, signed by Governor Jim Justice (R), requires hospital emergency rooms as well as other law enforcement and medical care providers to report suspected or confirmed drug overdoses to the Office of Drug Control Policy. Virginia HB 1532, signed by Governor Northam (D), has determined health education programs may include instruction on the safe use of and risks of abuse of prescription drugs.
Medicaid Expansion
The expansion of Medicaid continues to be a pertinent issue in the states as state policymakers wrestle with health care coverage policy decisions. Maine voters elected in November of 2017 to expand Medicaid, however lawmakers have been struggling to come up with a package to fund it. The Virginia General Assembly is in a special session now and with near-even partisan splits in each chamber, Democrats are optimistic something can pass. Lastly, barring the verification of the necessary 150,000 signatures, a Medicaid expansion ballot initiative will be in play for Utahns this November despite Governor Gary Herbert (R) signing a bill expanding Medicaid under the condition enrollees can prove they are working or volunteering.
What’s Next?
Despite many states having already adjourned and planning to conclude soon, a number of states see activity pick up in the spring months including: Louisiana, Minnesota, North Carolina, Oklahoma, and Pennsylvania. Additionally, there is always the possibility of special sessions as Virginia is currently in one over their budget and Medicaid expansion, while Florida may convene for one later this spring over gambling.
